Game Event System
A production-ready, visual event architecture for Unity that transforms chaotic event management into maintainable, testable workflows.
"I built this system because I was tired of battling 'invisible spaghetti code' in my own projects. As an indie developer, I needed a tool that balanced visual clarity with raw coding power—without performance trade-offs. TinyGiants is my commitment to professional-grade tools that I use in my own games every day." — [TinyGiants] from China
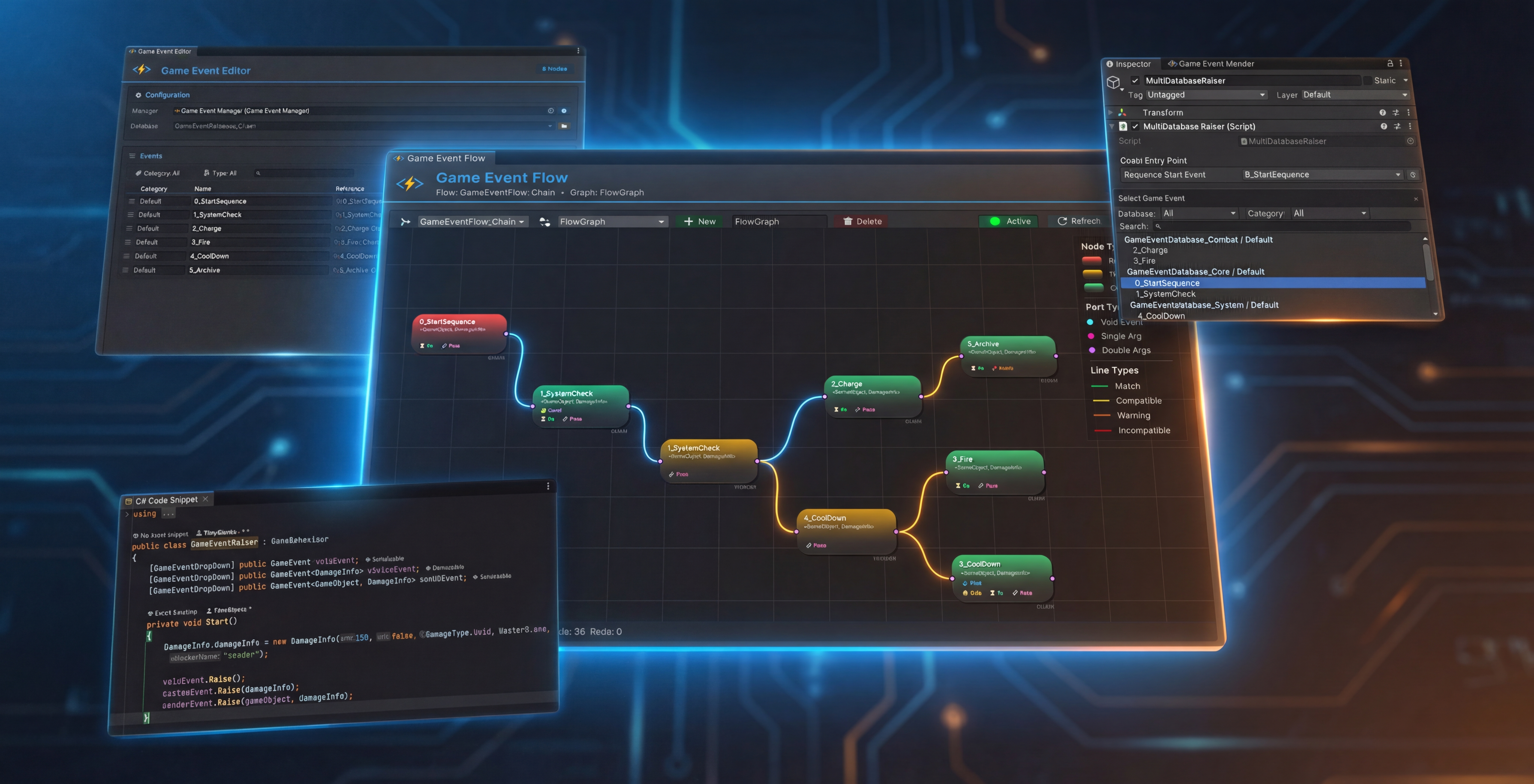
Why This System Exists
In traditional Unity development, events become invisible spaghetti:
- Hidden Dependencies: Who's listening? Where's it triggered? Good luck finding out.
- Runtime Breakage: Rename a method, break 10 scene objects.
- Cross-Scene Hell: Events die when scenes unload—memory leaks and null references everywhere.
- No Visibility: Complex event chains exist only in your head (and outdated comments).
TinyGiants.GameEventSystem provides a Visual-First, Type-Safe event architecture:
✅ Events as Assets - ScriptableObject-based, GUID-protected, survives refactoring
✅ Visual Flow Graphs - See your event chains, triggers, and conditions in one window
✅ Zero-Reflection Runtime - Expression Tree compilation for C++-like performance
✅ Designer-Friendly - Drag-and-drop binding, no coding required for simple workflows
✅ Production-Grade Tools - Real-time monitoring, reference finding, code generation automation
Core Philosophy: Hybrid Workflow
This system embraces a division of labor between programmers and designers:
| Role | Responsibility | Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Programmer | Define when events fire Raise() and what logic responds | C# API, Listeners |
| Designer | Wire events to scene objects and configure behaviors | Inspector Binding, GameEventBehavior |
| Tech Designer | Orchestrate complex sequences (delays, chains, conditions) | Visual Flow Editor |
Result: Clean separation of concerns with full visibility into event relationships.
Architecture Highlights
🏗️ Foundation: ScriptableObject-Driven
Unlike string-based or singleton event systems, events are first-class assets:
// Events are assets, not magic strings
[GameEventDropdown] public GameEvent onPlayerDeath;
[GameEventDropdown] public GameEvent<int> onScoreChanged;
void Die() {
onPlayerDeath.Raise(); // Type-safe, asset-referenced
}
Benefits:
- ✅ Complete Decoupling - Senders never know receivers. Fire once, notify many.
- ✅ Cross-Scene Persistence - Events survive scene loads/unloads.
- ✅ GUID Identity - Rename files, reorganize folders—references never break.
- ✅ Multi-Database Support - Modular organization for large teams.
📖 How GUID Protection Works
Every event has a unique GUID stored in .meta files:
# PlayerDeath.asset.meta
guid: a7f3c21e9b4d8f6e2d1a9c8b7e6f5a4d
Even if you rename PlayerDeath OnCharacterDied, Unity maintains the reference via GUID. No broken scene links.
🕸️ Visual Flow Orchestration
Stop hunting through code to understand event relationships. The Flow Editor turns invisible logic into maintainable graphs:
Use Cases
🎯 Triggers (Fan-Out)
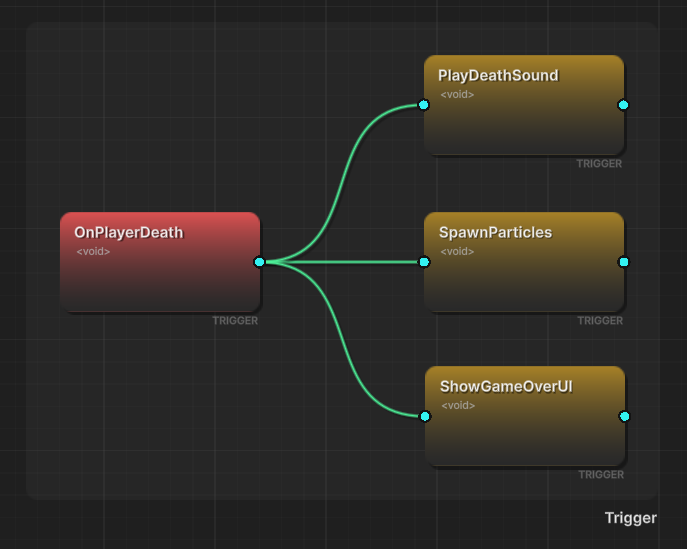
⛓️ Chains (Sequential)
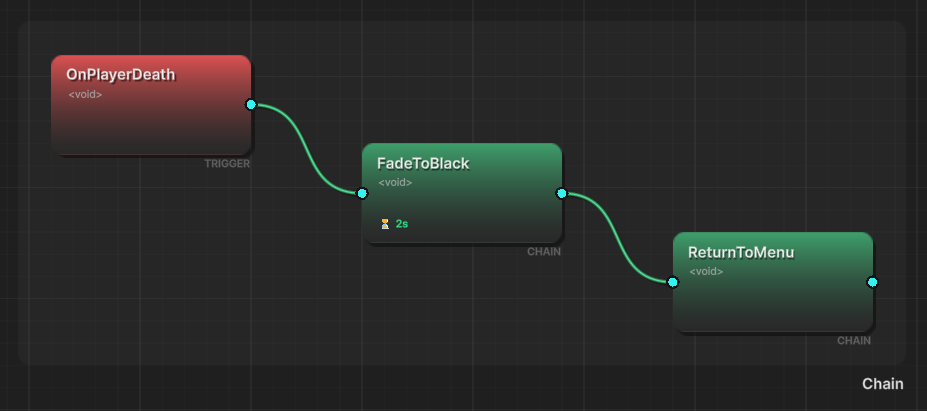
🔀 Hybrid Flows
Mix parallel + sequential logic
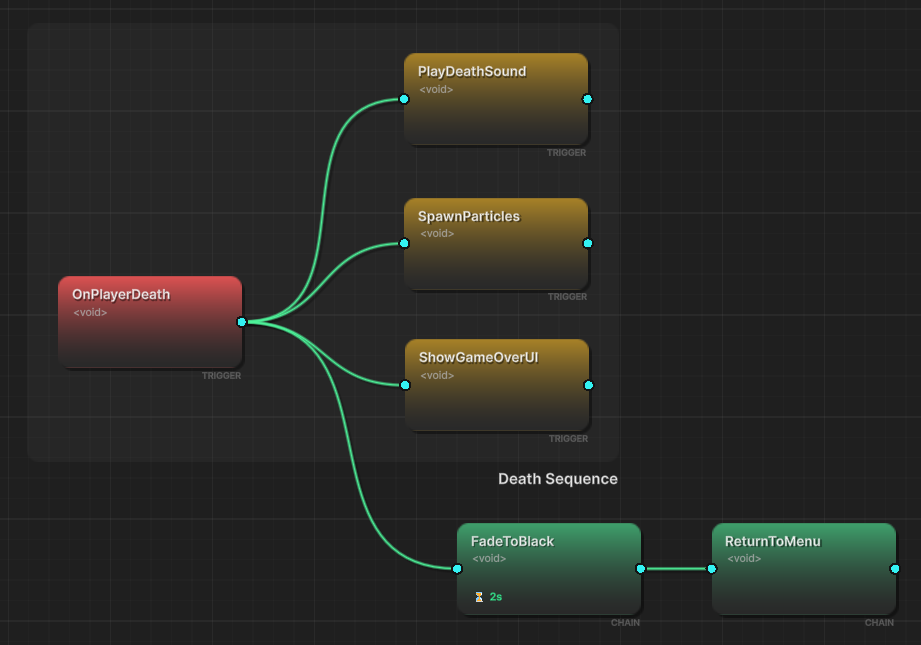
- Group Organization - Color-coded groups for large flows
- Real-Time Validation - Connection type checking (Green=Valid, Red=Error)
- Undo/Redo Support - Full history system (Ctrl+Z/Y)
- Runtime Debugging - Active nodes highlight in Play Mode
⚡ Type-Safe, Zero-Reflection Performance
Unity's generic serialization is broken by design. I fixed it.
The Problem
// ❌ Unity can't serialize this
[SerializeField] private GameEvent<PlayerData> onPlayerDataChanged;
Our Solution
// ✅ Auto-generated concrete class
[GameEventDropdown] public PlayerDataGameEvent onPlayerDataChanged;
// Generated code (automatic):
[Serializable]
public class PlayerDataGameEvent : GameEvent<PlayerData> { }
Performance Benefits:
- 🚀 Expression Tree Compilation - Conditions compile to delegates at startup (no runtime parsing)
- 🚀 No Reflection Cost - Direct method calls, not
Invoke() - 🚀 Native Inspector Support - Full
UnityEvent<T>compatibility
⚙️ Code Generation Workflow
- Select Types - Choose your custom types in the Creator window
- Generate - Click "Generate" to create concrete classes
- Compile - Unity auto-compiles the new code
- Create - Now you can create events for your custom types
Time investment: ~30 seconds. Benefit: Lifetime type safety.
Feature Matrix
⚓ Core Architecture
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Asset-Based Events | ScriptableObject architecture with GUID Identity—references survive renames and file moves. |
| Comprehensive Generics | Native support for GaneEvent<Void>, GameEvent<T>, and source-aware GameEvent<TSender, TArgs>. |
| Multi-Database System | Modular organization supporting multiple databases with Dynamic Loading and Health Checks. |
| Category System | String-based categorization for efficient fuzzy-search filtering within large event libraries. |
| Auto Static Reset | Automatic clearing of static caches in Editor Play Mode to prevent data pollution. |
🧠 Advanced Logic & Flow
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Expression Trees | Zero-reflection logic evaluation; conditions are compiled into high-performance delegates at runtime. |
| Visual Logic Builder | Construct complex nested AND/OR logic and dynamic property comparisons without code. |
| Hybrid Execution | Seamlessly mix parallel Fan-out Triggers and sequential Blocking Chains in one graph. |
| Argument Transformers | Dynamically extract and pass specific object properties as arguments between flow nodes. |
| Granular Flow Control | Per-node delays, Async/Coroutine waits, loop counts, and conditional execution gates. |
🎧 Listening & Binding
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Visual Binding | Drag-and-drop UnityEvent wiring in the Inspector with visual status markers and type safety. |
| Priority Listeners | Integer-based sorting ensuring critical systems react before standard UI/Audio listeners. |
| Conditional Listeners | Built-in Predicate support—callbacks only fire when specific logical criteria are met. |
| Persistent Listeners | Native support for cross-scene listeners that remain active during scene transitions. |
| Dynamic Runtime API | Full programmatic control to register or unregister listeners and manage Task Handles. |
📊 Tooling & Debug
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Dashboard & Wizard | Modern UI for Batch Operations and a fuzzy-matching Wizard for rapid event creation. |
| Code Automation | Tri-Mode CodeGen (Basic/Custom/Sender) with automatic compilation pipeline integration. |
| Reference Finder | Scene-wide scanner to pinpoint exactly which components reference specific event assets. |
| Runtime Monitor | Real-time profiling of Execution Time (Avg/Min/Max), listener counts, and GC allocation. |
| Automation Tree | Real-time visualizer for active Trigger and Chain hierarchies to debug complex logic flows. |
Performance Characteristics
Real-world metrics from production builds:
| Scenario | Performance | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Event Raise (0 listeners) | ~0.001ms | Virtually free |
| Event Raise (10 listeners) | ~0.02ms | No GC allocation |
| Condition Evaluation | ~0.003ms | Expression Tree compilation |
| Flow Node Execution | ~0.05ms | Includes coroutine overhead |
| Monitor Window (100 events) | ~0.3ms | Editor-only, no runtime cost |
Tested in shipped titles with 500+ events and 10,000+ listeners across scenes. Zero performance regressions.
🗺️ Navigation Roadmap
This map provides a complete overview of the system documentation. Use the tables below to quickly jump to the specific feature or tutorial you need.
- 🚀 Quickest Start: Jump straight to Example: Quick Start.
- 🎨 Visual Learner: Focus on the Visual Workflow and Flow Orchestration tables.
- 💻 Programmer's Deep Dive: Head directly to Runtime API.
🏁 1. Introduction
Foundational setup and core philosophy of the event-as-asset architecture.
| Page | Description |
|---|---|
| Project Structure | Understanding directory layout, folder protection, and modular organization. |
| Installation | Initializing the plugin and setting up the automated static reset pipeline. |
💎 2. Visual Workflow
Management tools designed to transform invisible code into a tangible visual dashboard.
| Page | Description |
|---|---|
| System Dashboard | Overview of the asset-based workflow and GUID identity system |
| Database & FlowGraph | Handling multi-database and multi-flowgraph setups and database health maintenance |
| Edit Game Event | Using the Dashboard for batch editing, search, and categorization |
| Create Game Event | Rapidly generating event assets using the fuzzy-search batch wizard |
| Configure Game Event | Mastering Inspector binding with visual status markers and type safety |
| Raise Game Event | Learn how to call events and enhance inspectors using the built-in GameEventDropdown Attribute |
| Find Game Event | Scanning scenes to locate component-level event dependencies. |
| Visual Condition Tree | Learn how to control the logic execution of event action through condition tree configuration |
🕸️ 3. Flow Orchestration
Visualizing and building complex multi-step logic sequences using nodes.
| Page | Description |
|---|---|
| Node Editor | Managing the GraphView canvas, groups, and snapshot-based Undo/Redo |
| Node Connector | Rules for hybrid execution modes and real-time connection validation |
| Node Behavior | Configuring node-level delays, loops, and argument transformation logic |
| Advanced Logic Patterns | Building no-code nested logic groups and conditional execution gates |
💻 4. Scripting & API
The developer's guide to high-performance C# integration and lifecycle management.
| Page | Description |
|---|---|
| Raising & Scheduling | Programmatic firing, delayed execution, and Task Handle management |
| Listening Strategies | implementing prioritized, persistent, and source-aware (Sender) listeners |
| Programmatic Flow | Using Expression Tree-based predicates for zero-reflection logic filtering |
| Best Practices | Architectural tips for clean decoupling and preventing data pollution |
| API Reference | Detailed technical documentation for all core classes and attributes |
🛠️ 5. Tools & Support
Automation and monitoring utilities for professional production environments.
| Page | Description |
|---|---|
| CodeGen & Cleanup | Using the Tri-Mode Generator and compilation pipeline automation |
| Runtime Monitor | Real-time performance profiling, deep logging, and warning systems |
| Community & Support | Accessing updates, reporting bugs, and getting technical assistance |
📚 6. Examples
Practical, ready-to-use scenes covering every scenario from basics to advanced API usage.
| ID | Example Page | Key Learning Point |
|---|---|---|
| 00 | Quick Start | The minimal workflow for creating, raising, and binding an event |
| 01 | Void Event | Using parameterless signals for global triggers like "Level Start" |
| 02 | Basic Types Event | Passing primitive data (int, float, string) through events |
| 03 | Custom Type Event | Leveraging CodeGen for serialized custom data classes and structs |
| 04 | Custom Sender Event | Using source-aware events to identify which entity raised the signal |
| 05 | Priority Event | Precisely controlling the execution order of multiple listeners |
| 06 | Conditional Event | Using predicates to execute callbacks only when criteria are met |
| 07 | Delayed Event | Managing timed logic and using Task Handles for cancellation |
| 08 | Repeating Event | Creating recurring pulse signals and automated logic loops |
| 09 | Persistent Event | Handling events during scene transitions (DontDestroyOnLoad) |
| 10 | Trigger Event | Bridging Unity's Physics system with Game Event assets |
| 11 | Chain Event | Building visual sequential logic using the Flow Orchestration graph |
| 12 | Multi Database | Isolating events into different assets for modular project organization |
| 13 | Runtime API | Registering and unregistering listeners dynamically via C# scripts |
| 14 | Runtime Monitor | Using profiling tools to debug execution timing and GC allocations |
For a hands-on start, we recommend following Example 00 (Quick Start) first, then exploring the Visual Workflow section to see how the editor tools can streamline your development.